Aquaculture: A Need for Innovation
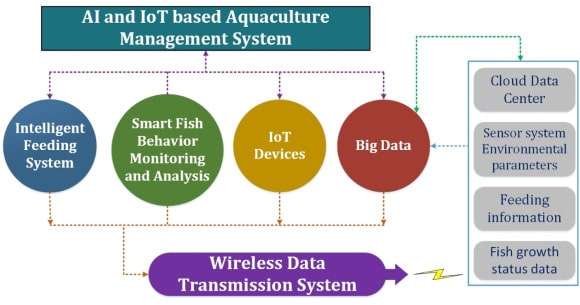 Source
Aquaculture, the controlled cultivation of aquatic organisms, has risen as a vital pillar in the global pursuit of food security. With a burgeoning global population and dwindling wild fish stocks, aquaculture offers a promising solution to meet the ever-increasing demand for seafood while alleviating pressure on fragile marine ecosystems.
As a practice that dates back centuries, aquaculture has evolved from simple fishponds to complex, technology-driven systems. Today, it encompasses a diverse range of species, from fish and crustaceans to mollusks and aquatic plants. The significance of aquaculture lies not only in its potential to provide a consistent protein source but also in its capacity to generate economic growth, create livelihoods, and bolster rural development.
In the quest for global food security, aquaculture stands as a beacon of hope. It marries the principles of responsible resource management with cutting-edge technology, contributing to a sustainable future where both human needs and the health of our planet are harmoniously balanced. As research, innovation, and best practices continue to shape the industry, aquaculture’s role in nourishing the world becomes increasingly crucial.
Source
Aquaculture, the controlled cultivation of aquatic organisms, has risen as a vital pillar in the global pursuit of food security. With a burgeoning global population and dwindling wild fish stocks, aquaculture offers a promising solution to meet the ever-increasing demand for seafood while alleviating pressure on fragile marine ecosystems.
As a practice that dates back centuries, aquaculture has evolved from simple fishponds to complex, technology-driven systems. Today, it encompasses a diverse range of species, from fish and crustaceans to mollusks and aquatic plants. The significance of aquaculture lies not only in its potential to provide a consistent protein source but also in its capacity to generate economic growth, create livelihoods, and bolster rural development.
In the quest for global food security, aquaculture stands as a beacon of hope. It marries the principles of responsible resource management with cutting-edge technology, contributing to a sustainable future where both human needs and the health of our planet are harmoniously balanced. As research, innovation, and best practices continue to shape the industry, aquaculture’s role in nourishing the world becomes increasingly crucial.
Predictive Analytics: A Game-Changer in Aquaculture
Predictive analysis, a powerful branch of data analytics, holds the key to unraveling the future from the patterns of the past. In a world where data is generated at an unprecedented rate, predictive analysis harnesses this abundance to forecast trends, behaviors, and outcomes. By examining historical data, identifying correlations, and leveraging advanced algorithms, predictive analysis empowers decision-makers with insights that transcend mere intuition. The essence of predictive analysis lies in its ability to turn data into actionable foresight. By analyzing vast datasets encompassing variables, timelines, and contextual information, it uncovers hidden relationships and trends. This process equips organizations across industries with the ability to anticipate market shifts, consumer preferences, and even potential risks.Disease Prevention and Management
Disease outbreaks pose a significant threat to aquaculture. The loss of entire fish populations can lead to severe financial repercussions and disrupt food supply chains. Here, predictive analytics equipped with AI algorithms step in. By analyzing historical disease data, water quality parameters, and environmental factors, predictive models can identify subtle patterns that foretell potential disease outbreaks. These models arm farmers with the ability to take proactive measures, such as adjusting water conditions, implementing targeted treatments, or altering feeding regimes, thus curbing the spread of diseases before they escalate.Optimized Feeding Strategies
Efficient feeding is the cornerstone of healthy aquatic organisms and sustainable aquaculture. Predictive analytics leverages AI’s data-crunching prowess to formulate optimized feeding schedules. By analyzing variables such as species type, size, growth rates, and environmental factors, AI-driven models can minimize feed wastage, reduce costs, and accelerate growth. This not only enhances economic viability but also aligns with responsible aquaculture practices by minimizing the ecological footprint associated with excess feed.Environmental Monitoring and Adaptation
Aquatic organisms are incredibly sensitive to environmental changes. Predictive analytics employs AI to process real-time sensor data and historical trends, enabling farmers to foresee shifts in temperature, oxygen levels, and water quality. This advance notice empowers aqua culturists to adapt operations proactively, ensuring the health and well-being of their stock. Consequently, this translates to minimized stress on aquatic ecosystems, fostering sustainable growth that safeguards biodiversity.AI vs. Predictive Analytics: Understanding the Synergy
While AI is a broad concept encompassing machine learning, neural networks, and more, predictive analytics is a specific application within the AI umbrella. AI equips systems with the ability to learn from data, adapt to new inputs, and perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. Predictive analytics, however, focuses on harnessing AI to predict future outcomes based on historical and real-time data. In the context of aquaculture, AI’s machine learning capabilities process complex data, learning from patterns to make informed decisions. This synergizes with predictive analytics, which uses these learned patterns to forecast future events, allowing aqua culturists to make strategic decisions that are both data-driven and forward-looking.Real-World Impacts and Success Stories
The adoption of predictive analytics powered by AI in aquaculture has yielded tangible results. Farms that have embraced predictive models have reported impressive reductions in disease-related losses. The reports not only demonstrate the potential of AI-driven predictive analytics but also underscore its capacity to reshape an entire industry.FAQs
Predictive analytics in aquaculture involves using historical data and advanced AI techniques to forecast future outcomes and trends. AI plays a crucial role by processing vast amounts of data, identifying patterns, and creating models that predict factors such as water quality, disease outbreaks, and optimal feeding strategies.
Predictive analytics enables aquaculture practitioners to make informed decisions that reduce waste, minimize environmental impact, and promote sustainable growth. By predicting disease outbreaks and water quality changes, farmers can take preventative measures, optimize resource allocation, and ensure responsible farming practices.
Data used for predictive analytics include water quality parameters, temperature, salinity, oxygen levels, feeding schedules, growth rates, and more. This data is collected through sensors installed in aquaculture facilities, remote monitoring systems, manual measurements, and automated data logging tools.
Predictive analytics can forecast the likelihood of disease outbreaks based on historical disease patterns and environmental conditions. It can predict optimal feeding schedules by analyzing growth rates and feeding habits. Additionally, it can anticipate water quality changes, helping farmers adjust conditions to prevent stress in aquatic organisms.
The accuracy of predictions in aquaculture depends on the quality and quantity of data available, the sophistication of the AI models used, and the specific factors being predicted. Generally, accurate predictions require a robust dataset and well-tuned algorithms. Over time, as the AI models learn from new data, their accuracy can improve.
While a basic understanding of aquaculture and data analytics is helpful, specialized technical knowledge is not always a prerequisite. Various software platforms and tools are being developed to simplify the integration of predictive analytics into aquaculture practices. However, collaborating with experts in aquaculture, AI, and data science can significantly enhance the effectiveness of predictive analytics implementations.
Final Thoughts
Predictive analytics fortified by AI has emerged as a formidable force of transformation in the aquaculture landscape. By harnessing historical and real-time data, predictive analytics empowers aqua culturists to preempt disease outbreaks, optimize feeding strategies, and adapt to environmental changes in real time. The synergy between AI’s learning capabilities and predictive analytics’ foresight function establishes a foundation for sustainable growth, aligning economic prosperity with environmental responsibility.
As we look ahead, the integration of predictive analytics and AI holds the promise of catapulting aquaculture into a new era of efficiency, innovation, and ecological consciousness. By embracing these technologies, the aquaculture industry stands poised to not only meet the demands of a growing global population but also to do so while safeguarding the delicate balance of our oceans and waterways.